3D Printing for Prototyping: Accelerate Your Development
Publish Date: 3 October 2025
3D Printing for Prototyping accelerates product development, cutting costs and lead times.
This guide is for US startups and product development teams looking to leverage 3D printing for rapid prototyping. We cover key considerations, common mistakes, implementation steps, and case studies for 3D printing in prototyping. Understanding how to use 3D printing for prototyping can significantly reduce costs and speed up product development. 3D printing is a key tool in prototyping, which is a crucial phase in product development.
At 3DDFM, BP Nel Consulting offers $75/hr expertise—half US rates—to help US startups prototype medical devices and consumer products. For example, our Medical Health Station prototype saved $2,000 in tooling costs. Thus, 3D printing ensures rapid, cost-effective iterations. Get a free audit at 3ddfm.com!
Summary: How Does 3D Printing Help with Prototyping?
- Enables rapid iterations and design validation, reducing development cycles by up to 30%.
- Cuts costs by minimizing tooling and material waste.
- Accelerates time-to-market by allowing quick production of functional prototypes.
Table of Contents
Why 3D Printing Matters for Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping refers to quickly creating physical models from digital designs to test and validate ideas. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, reducing development cycles by 30% and helping companies market faster by accelerating the entire product development process. For instance, printing a firearm accessory prototype can save weeks compared to traditional methods. This approach also improves cost efficiency by minimizing tooling costs, reducing the need for specialized labor, and enabling faster design iterations. Consequently, startups achieve faster market entry and lower costs. BP Nel Consulting’s 30+ years of expertise plus in-house Bambu Labs P1S printer ensures prototypes meet DFM (Design for Manufacturability) standards. Product development teams benefit from rapid prototyping with 3D printing by shortening lead times, lowering expenses, and enabling quicker design validation.
Key Considerations for Prototyping
3D printing optimizes prototyping, answering the Google top question, “How does 3D printing improve prototyping?”:
- Material Selection: Choose materials based on mechanical properties like strength, flexibility, and durability (e.g., PLA or ABS for cost and durability).
- Layer Resolution: Use 0.1mm for precision or 0.3mm for speed; adjust for optimal print and surface quality.
- Support Structures: Minimize supports to reduce material use and waste.
- Print Orientation: Optimize for strength and speed.
- Post-Processing: Plan for sanding or coating to enhance aesthetics and surface finish.
For example, our Rivian Roof Rail prototype used ABS for durability and was designed and refined using computer aided design (CAD software). Thus, 3D printing ensures efficient prototyping.

Common Prototyping Mistakes
Poor prototyping decisions waste time. Common mistakes include:
- Wrong Material Choice: Results in weak or expensive prototypes.
- Excessive Supports: Increases print time and material waste.
- Ignoring Post-Processing: Leads to poor aesthetics.
- Incorrect Orientation: Causes structural failures.
Thorough testing and collecting user feedback at each stage help avoid costly mistakes by identifying design flaws early, guiding iterative improvements, and ensuring prototypes meet user needs before final production.
For instance, a client’s unoptimized prototype cost $2,000 in rework. 3D printing avoids these pitfalls.
Steps to Implement 3D Printing
Implementing 3D printing requires a structured approach. The process enables multiple iterations and continuous refinement throughout the development process:
- Design Optimization
- Create a digital model and CAD models with DFM principles using Fusion 360 (a CAD software).
- Material Testing
- Test PLA/ABS for fit and strength.
- Slicer Configuration
- Set layer height and supports in Cura (a slicing software).
- Prototype Iteration
- Print multiple versions to refine designs, using physical prototypes and models. Collect user feedback and perform functional testing to ensure the prototype meets requirements.
- Validation
- Test prototypes for fit and function, emphasizing the importance of the testing phase and functional testing to validate design performance.
For example, our Barbeque Light prototype iterated twice, saving $2,000. Therefore, 3D printing accelerates development.
Once you have a structured process in place, choosing the right materials and technologies becomes the next critical step.

Materials and Technologies
Selecting the right materials and additive manufacturing technologies is crucial for a successful rapid prototyping process. The choice directly impacts the performance, appearance, and manufacturability of your functional prototypes, ensuring your product development cycle is both efficient and cost-effective.
Material Selection
- Choose from engineering plastics (e.g., ABS, PLA, PETG) or specialty materials based on prototype requirements.
- Consider mechanical properties, surface finish, and cost.
Additive Manufacturing Technologies
- Evaluate technologies such as FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), and SLM (Selective Laser Melting) for their suitability to your project. FDM uses thermoplastic filaments, SLS uses powdered materials fused by a laser, and SLM uses a laser to fully melt metal powders for high-performance parts.
With the right materials and technologies selected, it’s important to understand how these tools compare to traditional manufacturing methods.
Role of Technology in 3D Printing vs. Traditional Manufacturing Methods
Additive Manufacturing Methods
Techniques such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), selective laser sintering (SLS), and selective laser melting (SLM) enable advanced prototyping, including the use of metal powders for high-performance parts.
Slicer Software
Slicer software optimizes print settings for speed, balancing printing speed, surface quality, and structural integrity.
FDM Printers
FDM printers deliver cost-effective production and wide material compatibility, supporting various engineering and commodity plastics for flexible prototyping.
Resin Printing
Resin printing provides high-precision parts.
Specialized Equipment
Advanced 3D printers, laser cutting, and CNC machining enable rapid prototyping of complex geometries and high-tolerance components.
AI Optimization
AI optimization suggests material and orientation for improved results.
For instance, our Electrical Adapter used resin printing for precision, cutting costs by 20%. Thus, technology drives prototyping success.
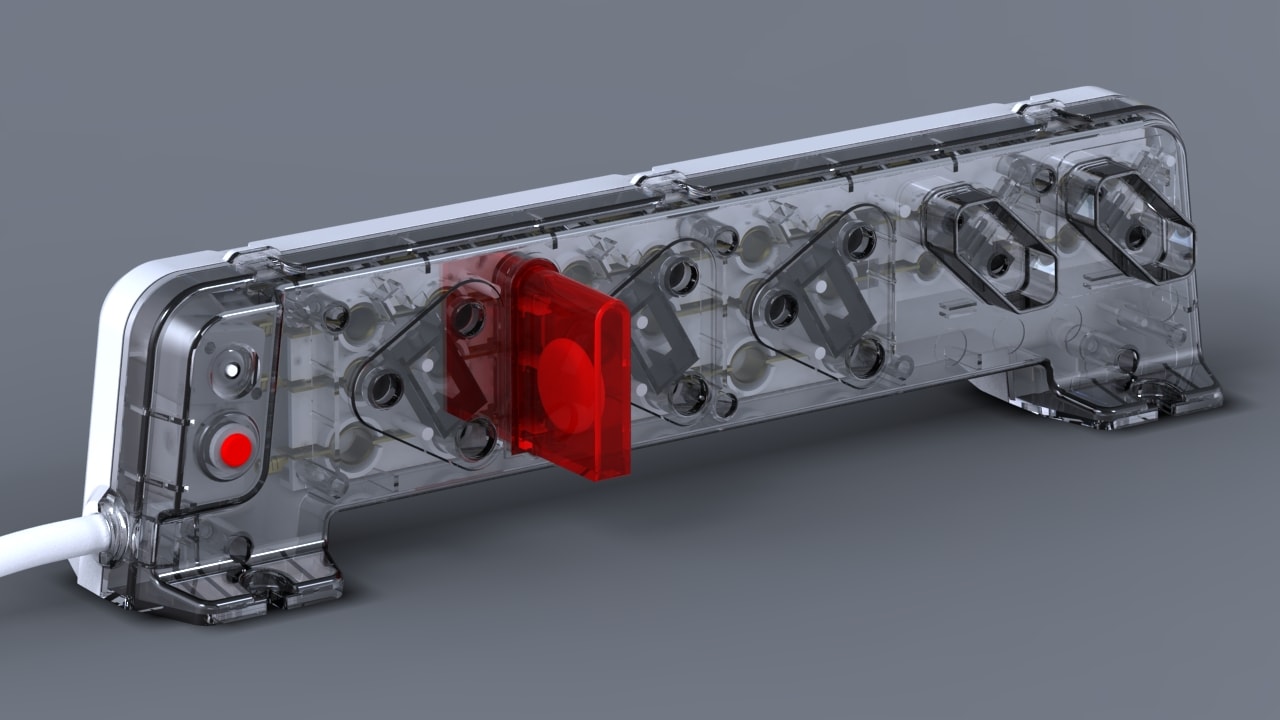
Case Study: Medical Device Functional Prototypes
Our Medical Health Station prototype showcases 3D printing success. The initial design risked $3,000 in tooling costs due to complex geometry. By leveraging 3D printing, we were able to produce complex geometries and select materials with enhanced mechanical properties, ensuring both design flexibility and functional durability. We applied 3D printing principles:
- Used ABS for durable prototypes.
- Optimized print orientation, reducing material by 25%.
- Iterated three versions in 72 hours, saving $3,000.
This approach delivered significant benefits, including accelerated design iteration, cost savings, and the ability to create intricate, customized components with high precision.
Continuous improvement and iterative improvements throughout the prototyping process were key to achieving a production-ready design that met all requirements.
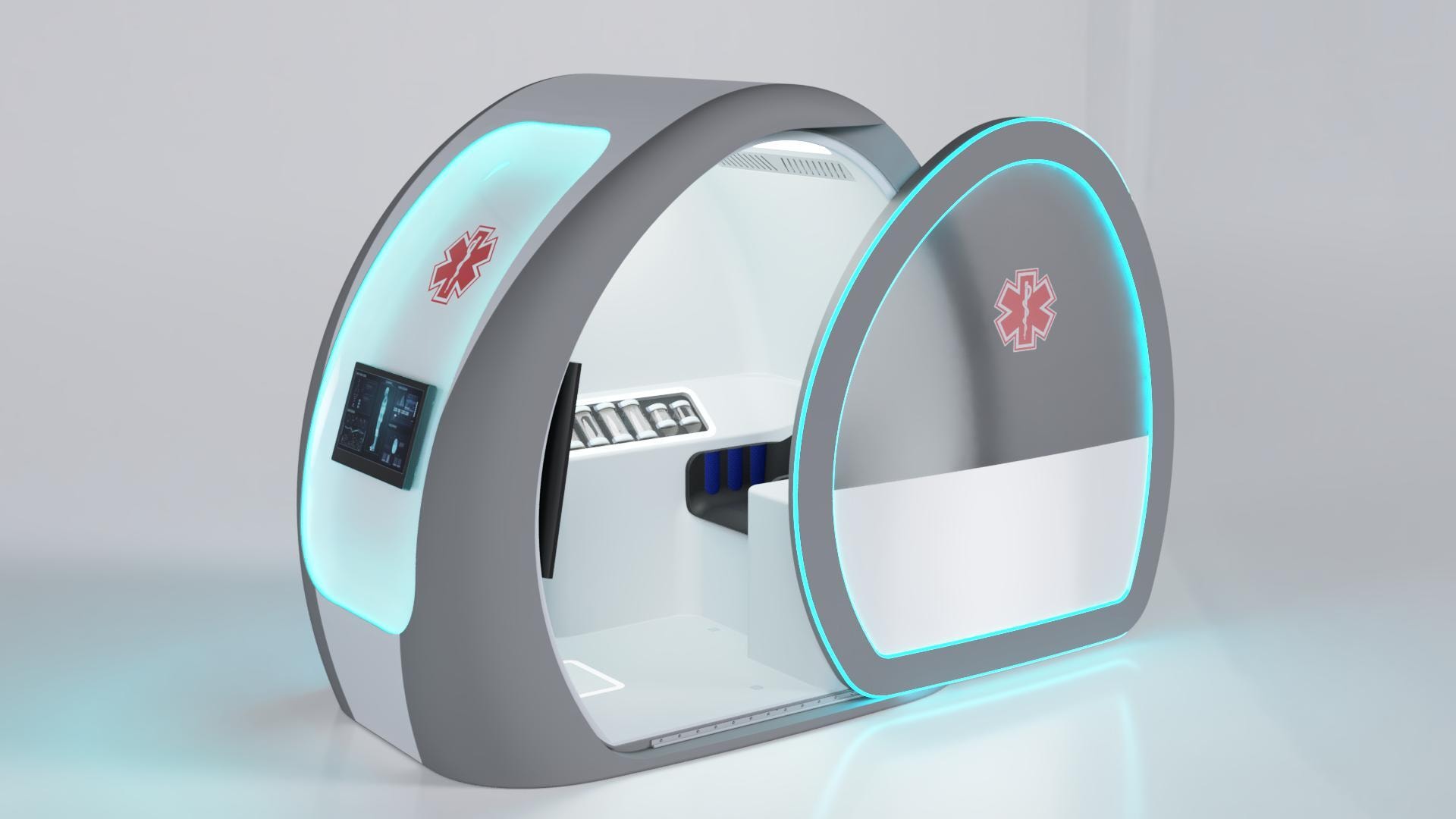

Watch the animation at Telehealth Station to see the design complexity. Get a free audit at 3ddfm.com.
FAQ: How Does 3D Printing Improve Prototyping?
3D printing improves prototyping by enabling rapid iterations, reducing material costs by 20-30%, and testing designs early, per Industry Insights. Prototyping with 3D printing is a rapid prototyping method and additive manufacturing method that streamlines the manufacturing process by translating digital designs into physical objects layer by layer. The choice and sourcing of raw materials are crucial, and 3D printing bridges the gap between prototyping and mass production by allowing prototypes to closely mimic final products, unlike traditional manufacturing and traditional manufacturing methods which often require expensive tooling and longer lead times. For example, printing a medical device prototype cuts lead times by weeks. 3D printing accelerates the development process and product development lifecycle by enabling valuable feedback, helping companies market faster, and reducing risks throughout the process.
Conclusion
3D Printing for Prototyping transforms development for US startups in medical devices and firearm accessories. As future trends in 3D printing continue to emerge, expect even greater advancements in materials, sustainability, and cost-effective production, making prototyping more accessible and efficient than ever. Partner with 3DDFM for $75/hr expertise, as shown in our Medical Health Station case study. Our 29+ years of experience ensures success. Get a free audit at 3ddfm.com!

